
Google AdSense is one of the easiest ways to create passive income from blogs, websites, and other online businesses. Along with affiliate marketing, it’s a longtime staple for blogging solopreneurs who want to make money.
Beginners love its low entry requirements and ease of implementation — but there are some things to know before you jump in.
In our ultimate guide we look at all aspects of the AdSense program: what it is, how it works, pros and cons, figuring out AdSense estimated earnings, and tips for maximizing your AdSense earnings.
What Is AdSense?
AdSense is a contextual advertising program run by Google. It’s designed to help advertisers expand their reach, and website publishers to make money with their content.
What does “contextual advertising” mean? Google quickly reads the content of any page that contains its AdSense code, every time someone views that page. Based on that content, Google supplies ads that are relevant — in context — to the page information.
For example, a page about dog grooming will show ads for grooming services, dog brushes, or nail trimmers.
Nowadays, AdSense also shows personalized ads. These are ads targeted to the individual visitor’s browsing history. If a person visits a site on power tools, for example, and then your site on dog grooming, Google might serve power tool ads to this visitor. You can opt out of showing personalized ads. This means that your visitors will only see ads relevant to your site’s content.
Who creates and pays for the ads? Advertisers who want to promote their products, i.e., participants in the Google Ads program (formerly called AdWords).
Here’s an example of a contextual ad. The ad fits the content of the page:
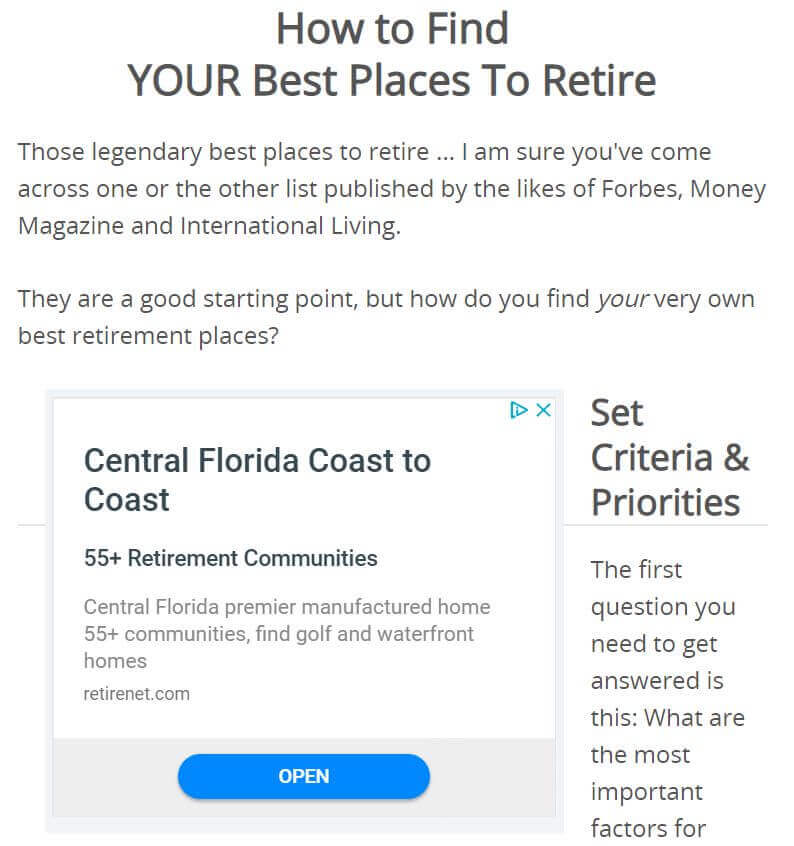
The second example shows a personalized ad. This ad is tailored to the visitor’s browsing history, not to the content of the page:
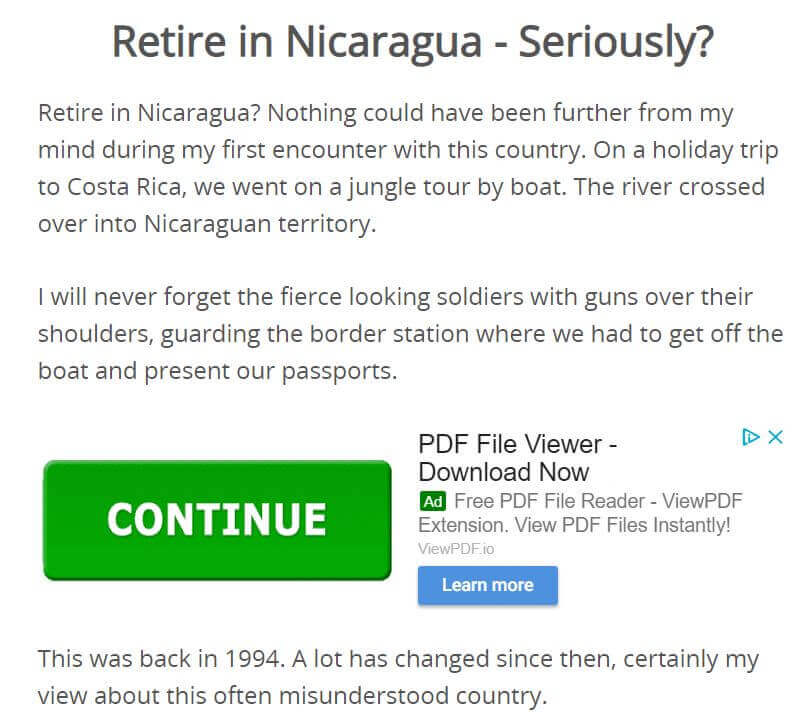
How Does AdSense Work?
It’s a simple 3-step process:
- Add the AdSense code into the code for your pages.
- Google displays the highest paying relevant ads on your website.
- When a visitor clicks an ad, Google pays you a percentage of what the advertiser is paying.
AdSense publishers receive 68% of the click cost and Google 32%. We’ll look more into how much you can earn with AdSense further down. But first, how do you get started?
Before You Apply for the AdSense Program, Do a Site Evaluation
Critically review your website or blog for these points:
- Does your site have enough pages with high-quality content? If you have fewer than 30 pages, keep creating more content before applying.
- Does your site have unique content? Duplicating other people’s content, or plastering your site with affiliate product content won’t cut it.
- Does your content comply with AdSense Program policies? For example, there’s a whole list of prohibited content, such as pornography, selling alcohol, tobacco, prescription drugs, and weapons.
- Does your site have a privacy policy?You must display a privacy policy on your website that discusses third-party cookies and how the visitor can opt out of any data collection.
- Is your website or a section of it directed to children under the age of 13? Then your site falls under the Children’s Online Privacy Protection Act (COPPA), and you must notify Google about it.
When you are satisfied that your site complies with Google’s guidelines, it’s time to apply for AdSense.
Create and Activate Your AdSense Account
Go to https://www.google.com/adsense/start and click “Get Started.” Enter your site’s URL and your preferred email address. Your email has to be associated with a Google Account. If you use any Google Services, e.g., Gmail or YouTube, you already have a Google Account. If not, you can create one during the sign-up process.
To fully activate your account, complete these three steps:
- enter your payment details
- verify your phone number
- connect your site
The last step is super important. It allows the Google crawler to access your site’s content and verify that it complies with the AdSense Program policies.
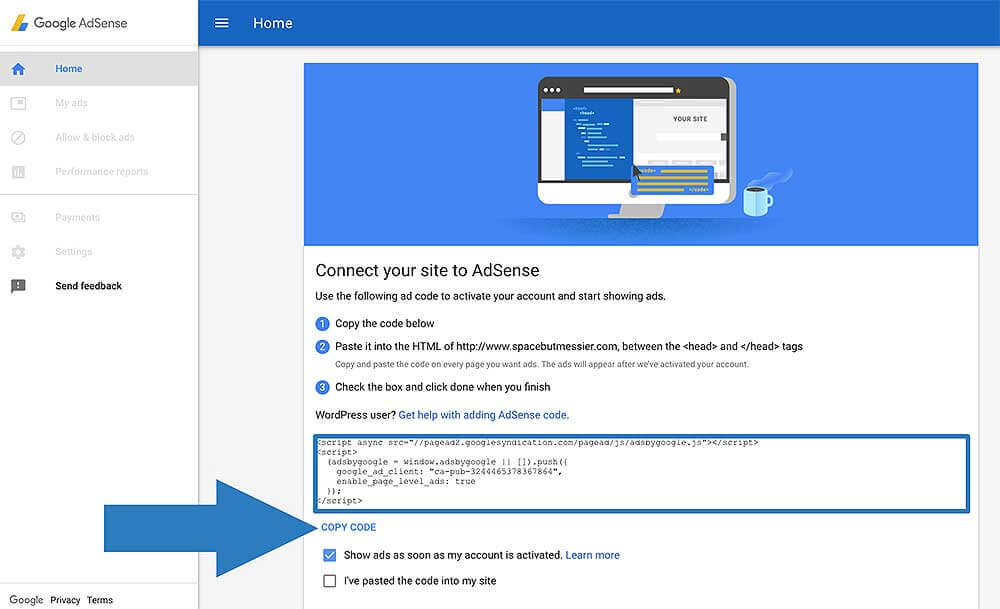
How do you connect your site?
Copy the code that you’ll see on the homepage of your new AdSense account and paste it between the <head> and </head> tags of one of your site’s content pages.
Google will send you an email when your account is fully activated. Then you can set up your ads and start earning money!
Set Up Your Ads
When setting up your ads, you can choose between “auto ads” and “ad units.”
Like the name suggests, “auto ads” are fully automated. You add the code once to every page where you want ads to show. Google determines where to display them and how many of them to show on the page.
If you love a hands-off approach and don’t mind handing over more control to Google, “auto ads” are for you. Many Solo Build It! members have reported higher earnings after switching to auto ads, but also an increased number of ads on their pages — which you may not be comfortable with.
If you want more control, set up “ad units.” With ad units you decide the ad size, format, and placement on your page. When you click on “Ads” > “Ad Units” in your AdSense account, you’ll see these five types:
- Display ads
- In-feed ads
- In-article ads
- Matched content
- Link ads
We suggest you get started with the two standard ad units: display and link ads.
Experiment with the rest once you have some experience. For “matched content,” your site needs to meet Google’s minimum requirements for traffic volume and the number of unique pages. When your site is eligible, this option will appear in your Google AdSense account.
Display Ads
Creating display ads is super easy:
- Select “Display ads” from the ad units dashboard
- Give your ad a name
- Click Create.
By default, “responsive” is selected under “ad size.” This means the ads automatically adapt their size to fit your page layout and your users’ devices.
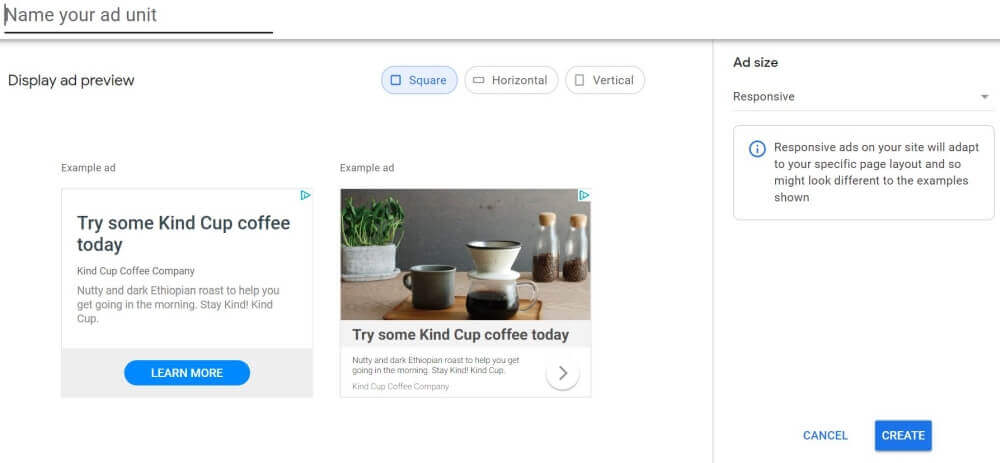
Google then generates the code for your ad. Copy the code and place it where you want the ad to appear on your page.
Although they’re called display ads, these ads can appear as text, image or even video. Gone are the days where you could choose between text or image ads.
If you prefer your ads to have a fixed size, you’ll find Google’s size guidelines here.
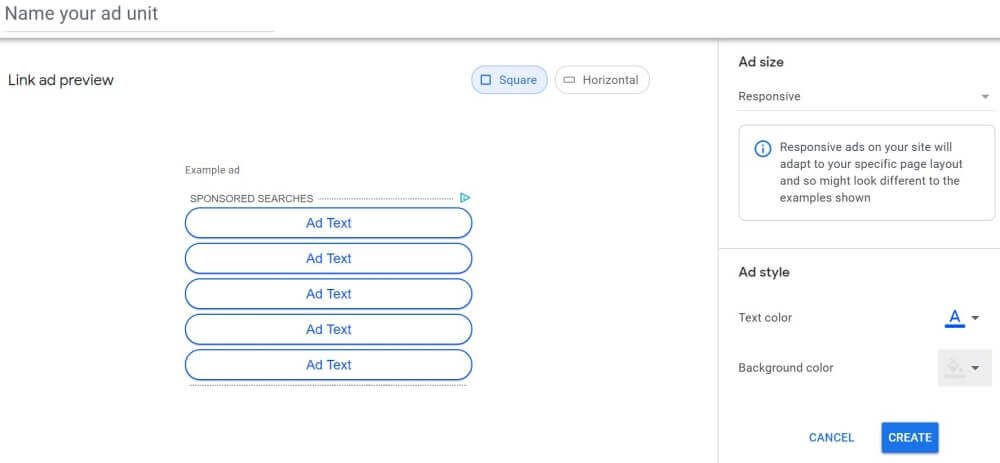
Link Ads

Link ads display a list of topics that may interest your visitor. On a site about Jamaica, for example, you may see a link ad-block showing topics like “jamaica vacation” or “car rental search.”
When your visitors click on a topic, they land on a page with search results and ads for that term.
When they click ads on that results page, you get paid. You won’t be paid for the initial click on the link ad.
Typical spots for link ads are the side columns (as vertical or square blocks) or below your site’s header (as horizontal blocks).
Create them the same way as display ads. You’ll have the choice between responsive link ads (recommended by Google) and fixed sizes.
Pros and Cons of Making Money With Google AdSense
You now have an idea about how to make money with Google AdSense. But what are the pros and cons of monetizing your blog with AdSense, and how does it compare to other methods?
Let’s look at the pros first:
- The AdSense program is free and easy to join.
- There are no minimum traffic or page view requirements (except for certain ad types like “matched content”).
- Setting up ads is straight-forward. Your time investment is minimal, especially if you opt for “auto ads.”
- Your ads don’t require any maintenance after the initial set-up.
- You get paid monthly by direct deposit, check or Western Union Quick Cash (after you reach the $100 minimum threshold).
- You have access to top-notch reporting features and optimization tips by Google.
Overall, AdSense provides an excellent passive income option for your blog — if you get enough traffic.
Which brings us to the first of the disadvantages:
- You need a large amount of traffic to make a significant income with AdSense.
- When a visitor clicks an ad, she leaves your site, and you lose the opportunity to make money with your own products or higher-paying affiliate products.
- Google can terminate your account at any time if they believe you’ve violated their policies.
- You may simply not like the look of the ads on your pages.
How does AdSense compare to other ways of making making money with your blog? It is by far the easiest monetization method for beginners. But the price for this easy to use option is the low income potential per visitor.
Best Practices for Maximizing Your AdSense Earnings
Before we dive into the tips, let’s look at how the Google AdSense estimated earnings are calculated. Here’s the basic formula:
Earnings = Page Views x Click-Through Rate (Page CTR) x Cost Per Click (CPC)
- Page Views only includes those pages with Google’s ads on them. If you have 1,000 visitors viewing two pages each on average, that gives you 2,000 page views. If only half the pages contain ads, AdSense will report 1,000 page views.
- Page CTR is the percentage of clicks divided by Page Views. If 1,000 page views generate 10 clicks, your click-through rate is 1% (10/1,000 x 100).
- CPC is how much each click earns you, on average. If your CPC is $0.50, your total earnings will be $5.00 (10 clicks x $0.50).
An even simpler formula is just: Clicks x CPC = revenue.
How much can you earn? That depends on various factors, including how many visitors you get, how many pages they visit, where they come from (traffic from the U.S. is “worth” more than from India, for example) and what your niche is (ads about finance pay more than ads about pets, for example).
AdSense gives an indication for earning potential on their home page. Select region, content category, and monthly page views to see the potential annual revenue.
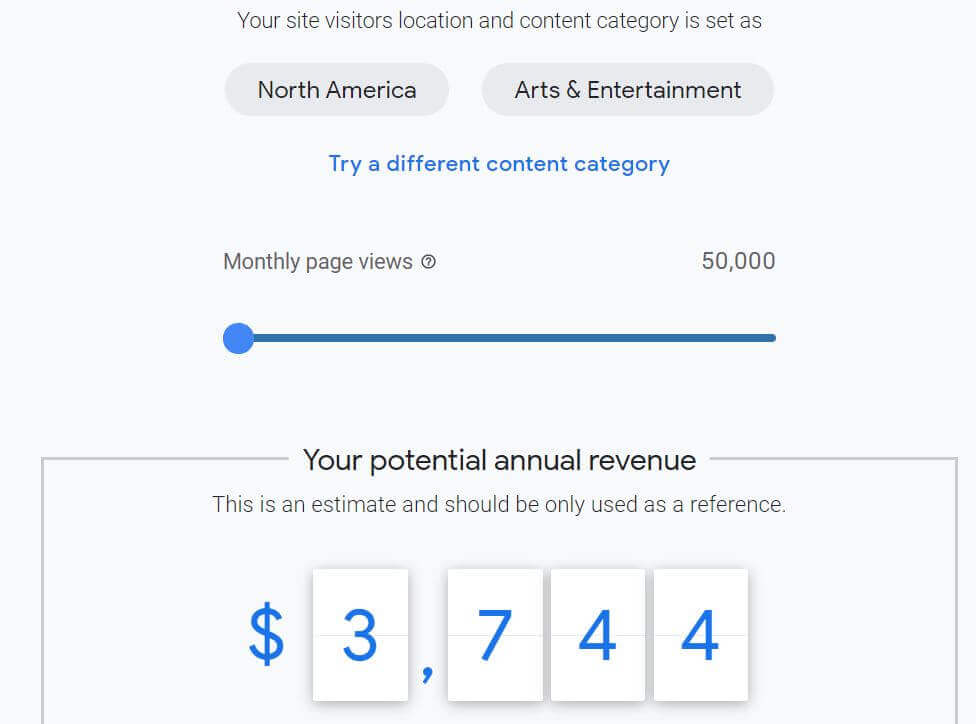
The starting point for Google’s own AdSense calculator is at 50,000 page views per month! This should give you an indication of the amount of traffic you need to make your AdSense earnings worthwhile.
Want to play around with some more numbers? Here’s another neat AdSense calculator.
Apart from increasing your website’s traffic, what else can you do to maximize earnings? Here are our top three tips:
Tip 1: Strike the Right Balance Between Content and Ads
The main thing visitors should see when they land on your page is your high-value content. Yes, you want to position AdSense units where they’re most likely to receive clicks, but overwhelming the content with advertising (this includes other ads, not just AdSense ads) is a no-no.
Too many ads creates a bad user experience for your visitors. And even if ad-heavy content does result in higher earnings, it will not last — search engines will penalize your site, especially if ads show “above the fold” (on the first screen) of mobile devices.
Google recognizes that this is a tough challenge for publishers, so they introduced an ad balance control. It allows you to reduce the number of ads shown on your pages. Google claims the effect on your earnings to be minimal because they specifically reduce showing the ads that earn you the least revenue.
Should you use the ad balance control? More about this in the next tip.
Tip 2: Test, Test, Test
Test to determine what works (and what doesn’t) and keep the best. Two ways to test are custom channels and AdSense experiments.
Custom channels allow you to track the performance of specific groups of ad units. For example, you could test ad formats (rectangle vs horizontal), ad location (left vs. right; middle vs. bottom) or specific page topics (pages about dog grooming vs. dog breeds).
AdSense experiments (on the “Optimization” tab) allow you to compare the performance of different ad settings. They work by splitting your site’s traffic between the two ad settings so that their performance can be measured side by side.
In the past, you could split test ad sizes, link colors, background colors, and other ad elements. Now you can only test blocking controls and the above mentioned ad balance controls. The experiments are super easy to set up, so it’s worth using them.
Tip 3: Focus on Your Most Wanted Response (MWR)
Each of your pages should be designed around a “most wanted response” (MWR) from your visitors.
Your page’s MWR is to buy an ebook? Don’t distract your visitors with ads or affiliate links.
Your page’s MWR is a click on an affiliate link? Consider showing fewer ads, or none at all.
And if your MWR for a page is a click on an AdSense ad, give them their best shot at getting the highest possible click-through rate. How? Show at least one ad “above the fold,” but within your content.
“Above the fold” means the ad is visible without scrolling. And “within the content” means the ad isn’t in your header or sidebar, but in your main content column. After the first paragraph is usually a good spot.
But keep in mind the warning mentioned above: do not show ads above the fold on mobile devices. Google will penalize your site with lower search rankings if it detects ads above the fold.
Ready to Get Started With Google AdSense?
This monetization model is where a lot of people start as they build towards making a living blogging. Now you’re ready to try it on your website. We’ve covered a lot of ground in our AdSense beginner’s guide:
- What AdSense is and how it works.
- How to do a site evaluation before you apply to the program.
- How to create and activate your account.
- The difference between “auto ads” and “ad units” and how to set them up.
- The pros and cons of using AdSense.
- How to calculate your potential earnings.
- Three top tips for maximizing your AdSense earnings.
Want more time-tested tips for making the most out of AdSense (without violating Google’s guidelines)? Download our free cheatsheet, “18 Google AdSense Tips to Boost Your Earnings (And Avoid Getting Banned).”

Latest posts by Margit Streifeneder (see all)
- From Traffic Peaks to Auto-Pilot: A Psychologist’s Website Success Story - March 27, 2025
- From Swim Teacher to Solopreneur: Building Passive Income Online - February 27, 2025
- From Concierge to Global Tours: 10 Lessons for Travel Business Growth - December 19, 2024


